
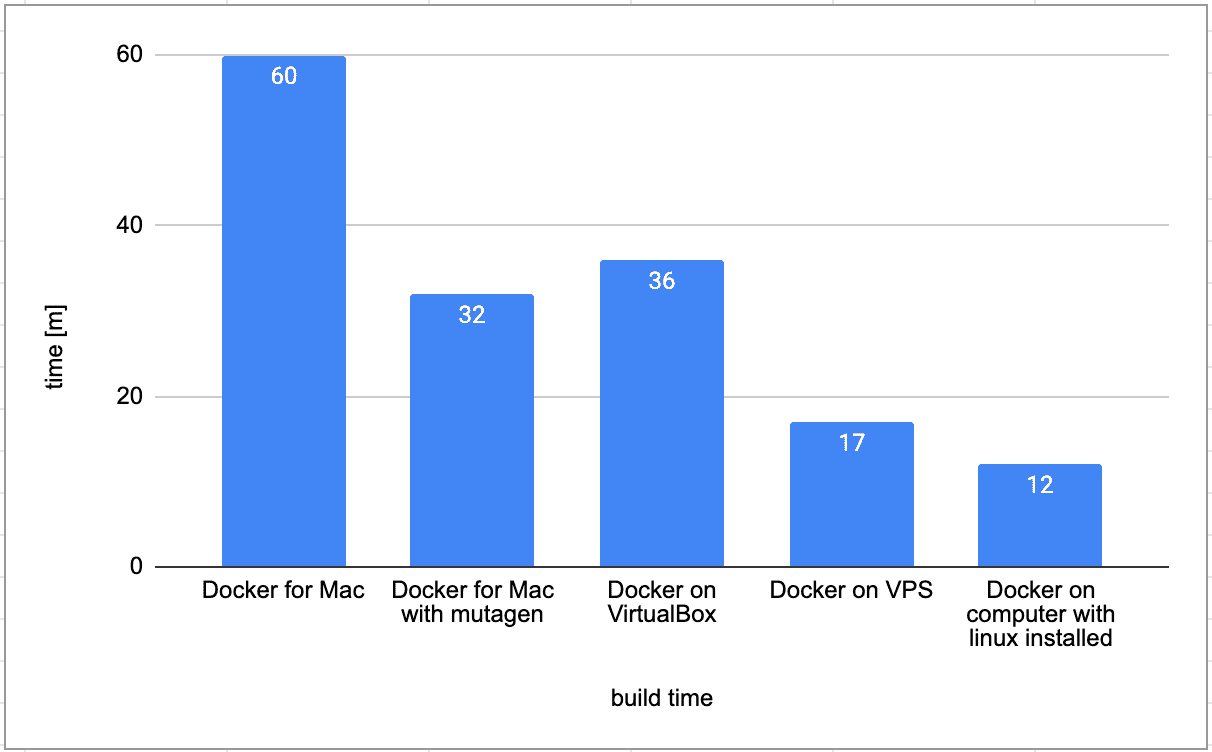
All of the processes, including system daemons, run in containers, enabling users to assemble a Linux subsystem with only the needed services. Salesforce next to be certified on Microsoft Azure?ĭocker claimed LinuxKit allows users to "create very secure Linux subsystems because it is designed around containers.Docker libcontainer unifies Linux container powers.Gambling on virtualization: One company's mission to automate its infrastructure.To help you decide whether containers and Docker are right for your team, see this article on the Sitecore Knowledge Center. However, for an organization, there are other considerations. There are many benefits for Sitecore developers. Use docker-compose down and docker-compose up to get up and running again. When you containerize your build, you have complete control of the build environment.Įnvironment stability - because containers are immutable, you do not have to worry about ruining your local Sitecore instance.
DOCKER CONTAINER FOR MAC INSTALL
Simplified onboarding - the onboarding process is as simple as: install prerequisites, clone your code repository, run docker-compose up.Įnvironment consistency - eliminate issues due to environment inconsistencies. You can start and stop entire instances quickly when jumping between projects. Multi-project efficiencies - you can run multiple Sitecore instances simultaneously without worrying about things like conflicting versions of SQL and Solr.
DOCKER CONTAINER FOR MAC DOWNLOAD
You can get an instance up and running with docker-compose up, and container images will download automatically. Sitecore provides container images ready to use. No install - no installation using SIF (Sitecore Install Framework), SIM (Sitecore Instance Manager), and so on. Kubernetes is the most used, and it is well supported by Microsoft through the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). It helps you deploy and manage containers in production. Orchestrator - a management tool for containers. After you create the definitions, you can deploy the entire multi-container application with a single command ( docker-compose up). You use it to define how multi-container applications run. It consists of the contents of a Docker image, an execution environment, and a standard set of instructions.Ĭompose - a CLI tool and (YAML based) text document format created by Docker. If you do not specify a tag, Docker defaults to the tag name latest.Ĭontainer - an instance of an image. In an image reference, this is the part after the final colon, and it is often used for a version number or architecture variant, for example, ltsc2019 in /windows/servercore:ltsc2019. Tag - a reference to a specific image within a repository. In an image reference, the repository is the part before the final colon, for example, /windows/servercore in /windows/servercore:ltsc2019. Repository - a collection of images with the same name, labeled with tags to indicate the version or variant. A registry contains one or more repositories. This can be either public ( Docker Hub) or private ( Azure Container Registry). Registry - a place where you store images. This file is used by the Docker CLI build command to build the image. An image is immutable once it has been created.ĭockerfile - a text document format that contains instructions for assembling a Docker image.
An image is often based on another image, with some additional customization. Image - a package with all code and dependencies that serves as the blueprint for creating a container.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
